Architecture
This section describes the core components and flow of the cdk-erigon configuration across its three main deployment modes: sovereign, validium, and zkRollup. These configurations vary primarily in data availability and prover setup, while sharing the same core Erigon-based client and bridge infrastructure.
cdk-erigon-sovereign¶
| Component | Description / Link |
|---|---|
| Execution + Consensus Layer | CDK-Erigon — Combined Ethereum client for execution and consensus |
| AggKit - Oracle | AggOracle — Updates global Ethereum Root (GER) |
| AggKit - Sender | Sends certificates to Agglayer |
| Bridge API | zkEVM Bridge Service — Enables messaging between chains |
| Ethereum Bridge Contracts | zkEVM Contracts — Settlement layer contracts on Ethereum |
| Agglayer Network | Agglayer — Aggregation layer for certificates and proofs |
| Agglayer Node — Participates in Agglayer | |
| Agglayer Prover — Generates validity proofs |
cdk-erigon-zkrollup¶
| Component | Description / Link |
|---|---|
| Execution + Consensus Layer | CDK-Erigon |
| Internal CDK Infrastructure | Sequence Sender and Aggregator |
| Bridge API | zkEVM Bridge Service |
| Ethereum Bridge Contracts | zkEVM Contracts |
| Data Availability Layer | On-chain data submitted directly to Ethereum (no off-chain DAC) |
| Agglayer Network | Agglayer, Agglayer Node |
| Prover Network | Hermez Prover — zk-SNARK based proof generator |
cdk-erigon-validium¶
💡 Note: This mode shares the same architecture as
zkrollup, but uses an alternative data availability (DA) layer.
| Component | Description / Link |
|---|---|
| Execution + Consensus Layer | CDK-Erigon |
| Internal CDK Infrastructure | Sequence Sender and Aggregator — build and send transaction batches |
| Bridge API | zkEVM Bridge Service |
| Ethereum Bridge Contracts | zkEVM Contracts |
| Data Availability Layer | Custom DAC — Off-chain data availability committee |
| Agglayer Network | Agglayer, Agglayer Node |
| Prover Network | Hermez Prover — zk-SNARK based proof generator |
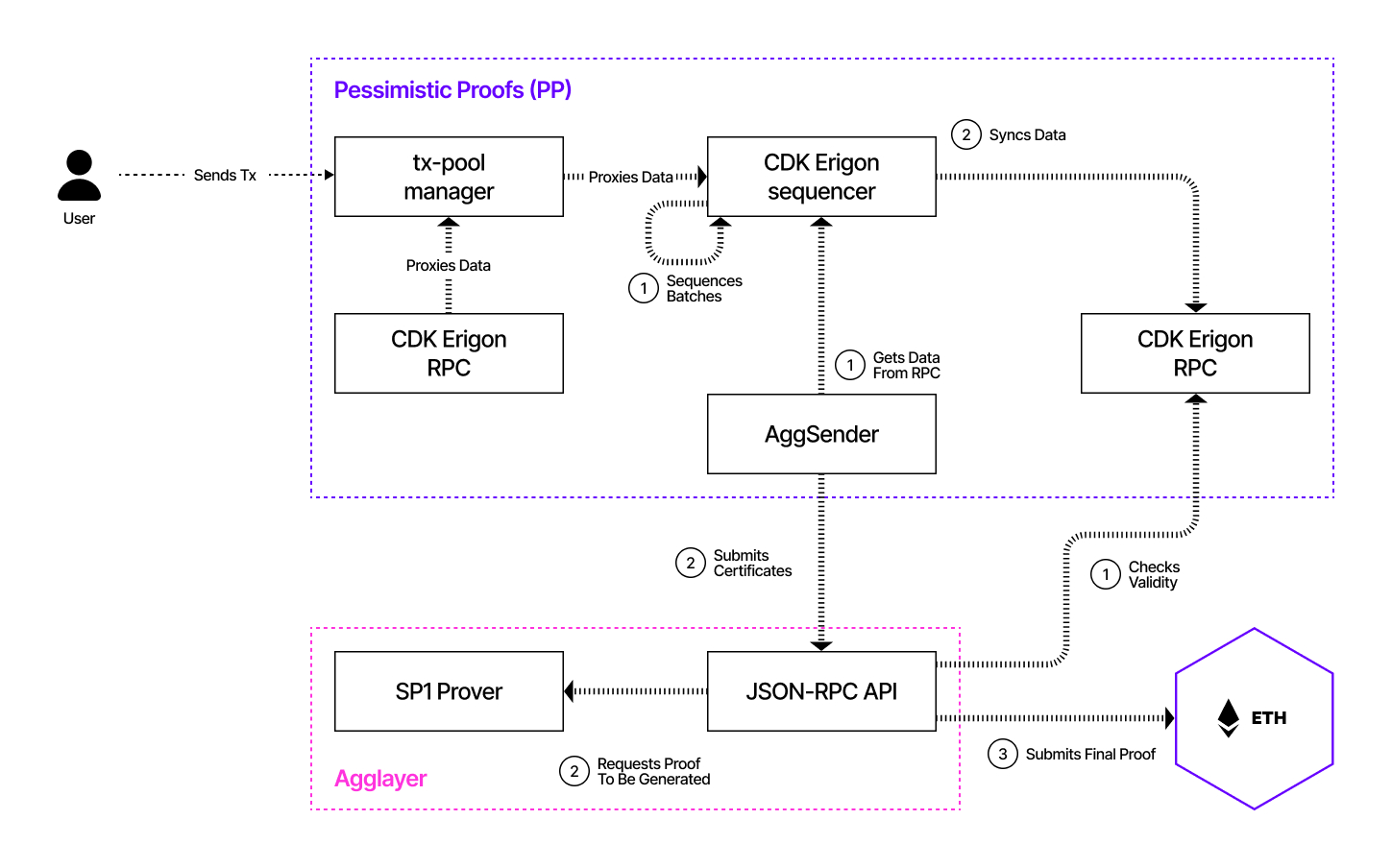
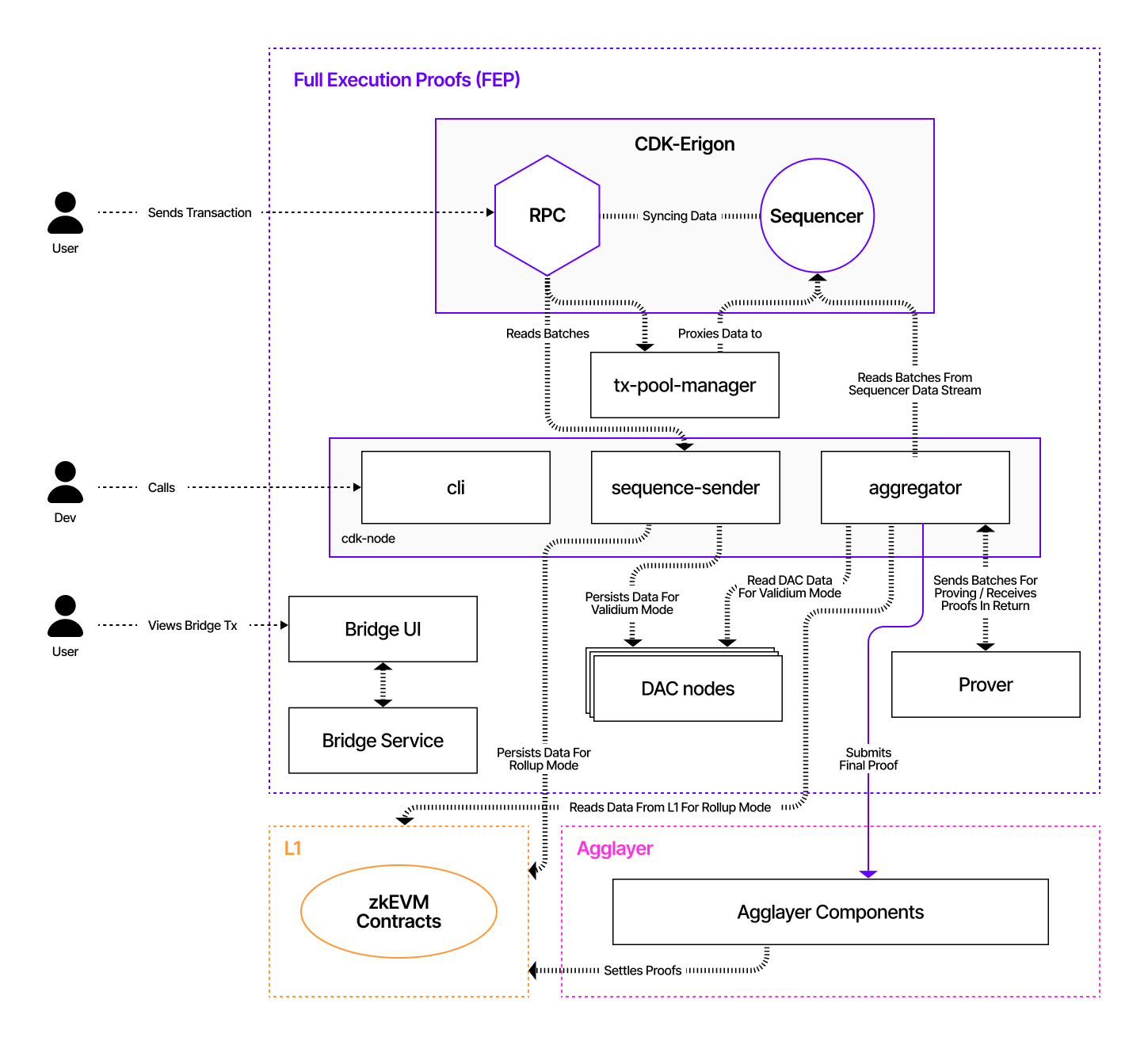
User Data Flow¶
The following diagram sequentially depicts the user data flow for the CDK FEP config in validium mode using a mock prover and an Agglayer connection.
Sequential Interactions¶
- The user sends a transaction to the CDK Erigon RPC node.
- The CDK Erigon RPC node proxies the data to the CDK Erigon sequencer node and syncs the batch data between the sequencer and the RPC nodes.
- The sequencer sequences the transaction batches.
- The sequencer sender reads batches from the RPC node.
- In validium mode only, the sequencer sender persists transaction data into the DAC nodes.
- The sequencer sender sequences the batches into the L1 smart contracts.
- The aggregator reads batches from the sequencer data stream.
- The aggregator sends batches to the provers.
- The aggregator submits the final proof to the Agglayer.
- The Agglayer submits the final proof to the L1 smart contract domain.
Mermaid Sequence Diagram¶
sequenceDiagram
participant User
participant ErigonRPC as CDK Erigon RPC Node
participant Sequencer as CDK Erigon Sequencer Node
participant SeqSender as Sequencer Sender
participant Aggregator
participant Agglayer
participant DACNodes as DAC Nodes
participant Prover
participant L1 as L1 Smart Contracts
User->>ErigonRPC: Send transaction
ErigonRPC->>Sequencer: Proxy and sync transaction data
Sequencer->>Sequencer: Sequence transaction batches
SeqSender->>ErigonRPC: Read batches
SeqSender->>DACNodes: Persist transaction data (validium mode only)
SeqSender->>L1: Sequence batches into L1 Smart Contracts
Aggregator->>Prover: Send batches to Prover
Prover->>Aggregator: Return proofs
Aggregator->>Aggregator: Aggregate proofs
Aggregator->>Agglayer: Submit final proof
Agglayer->>L1: Submit final proof to L1 Smart Contract Domain